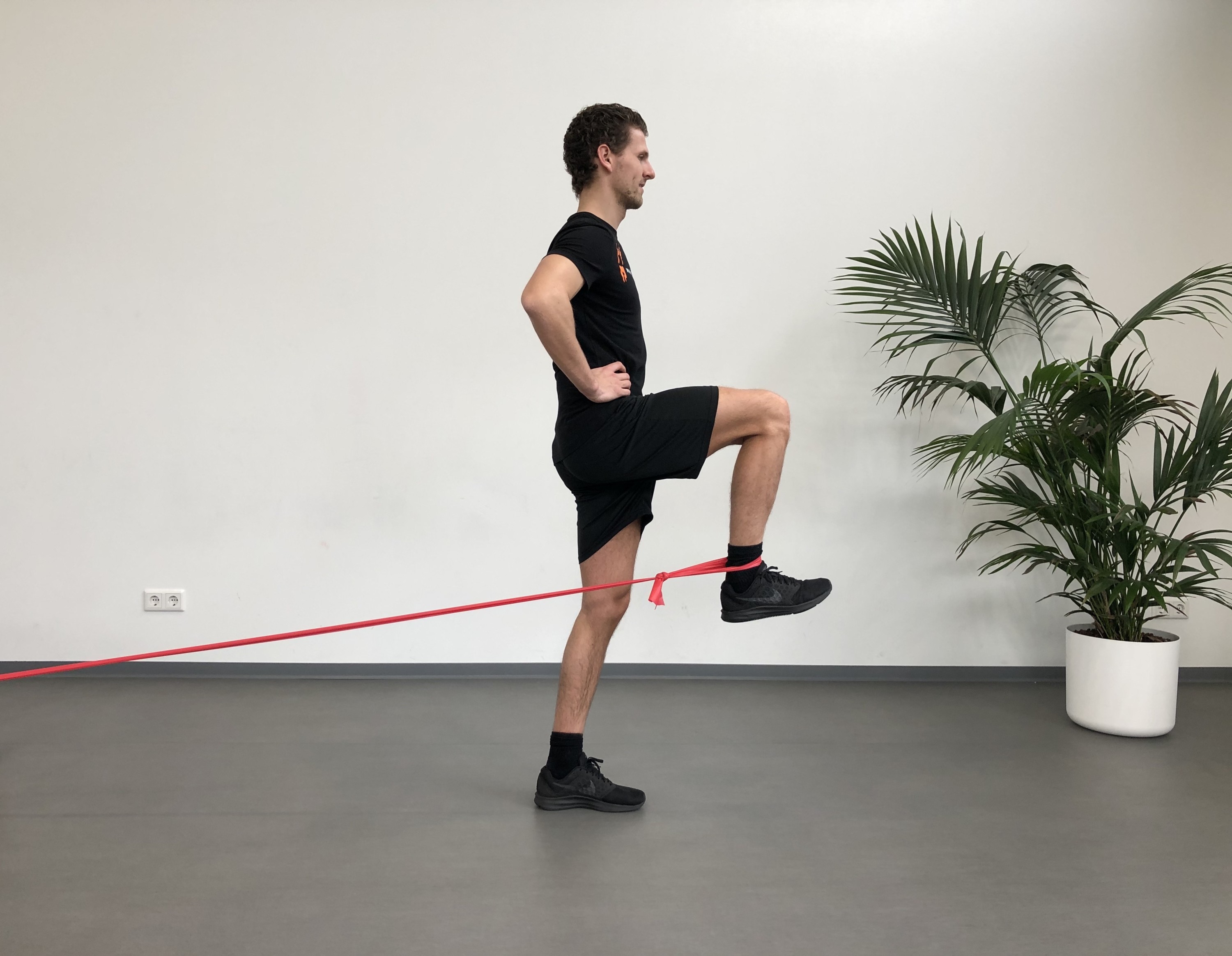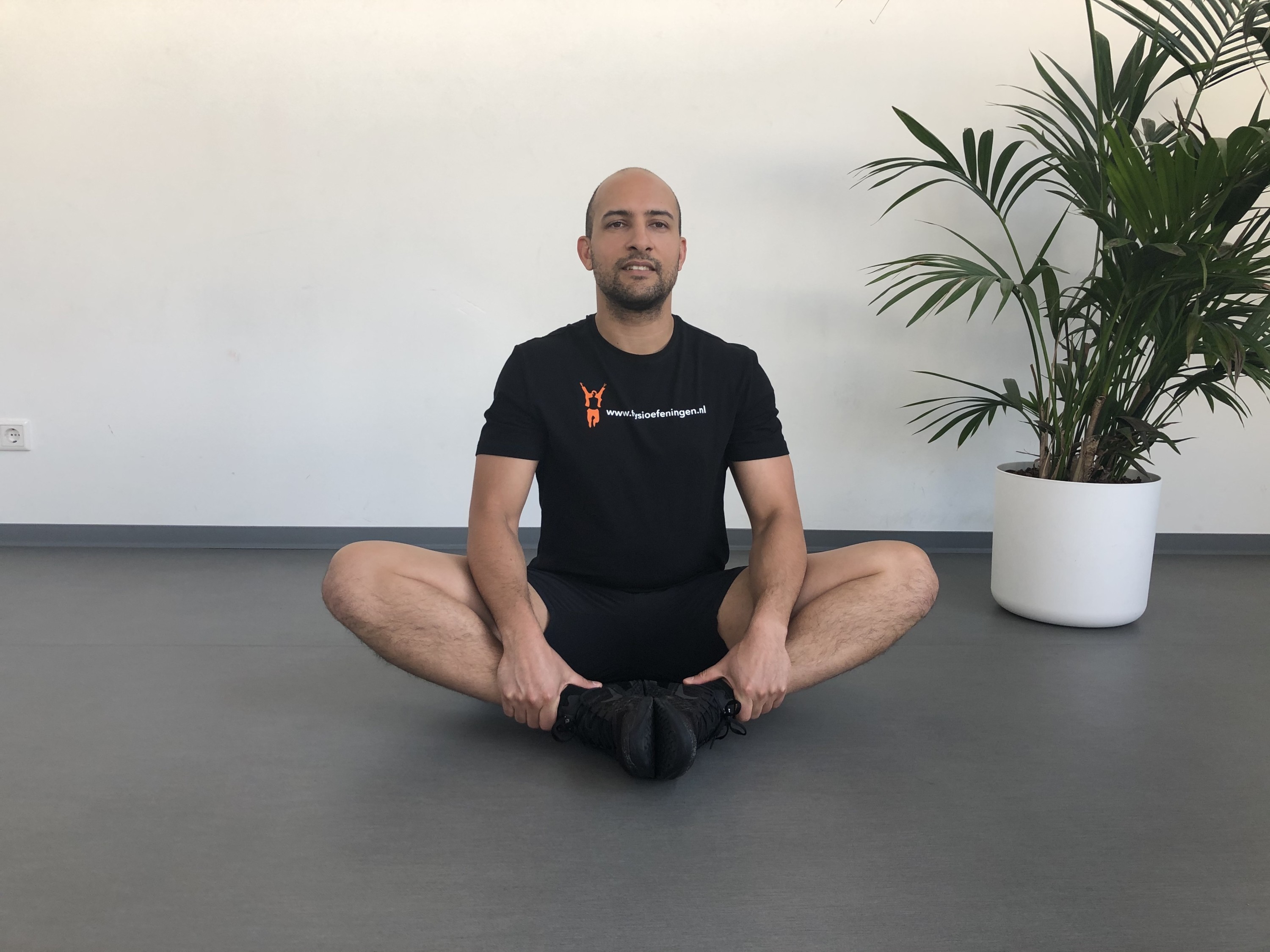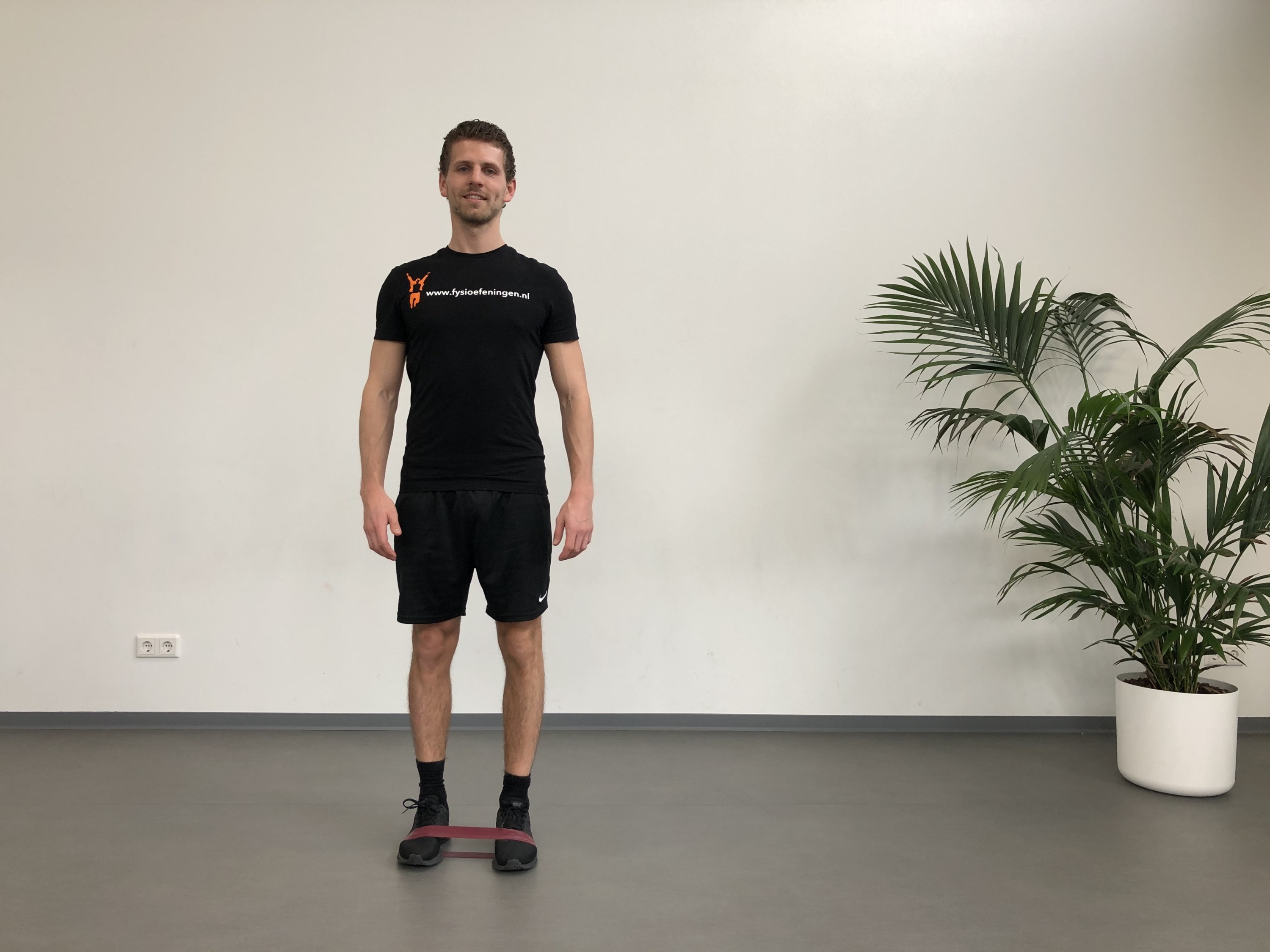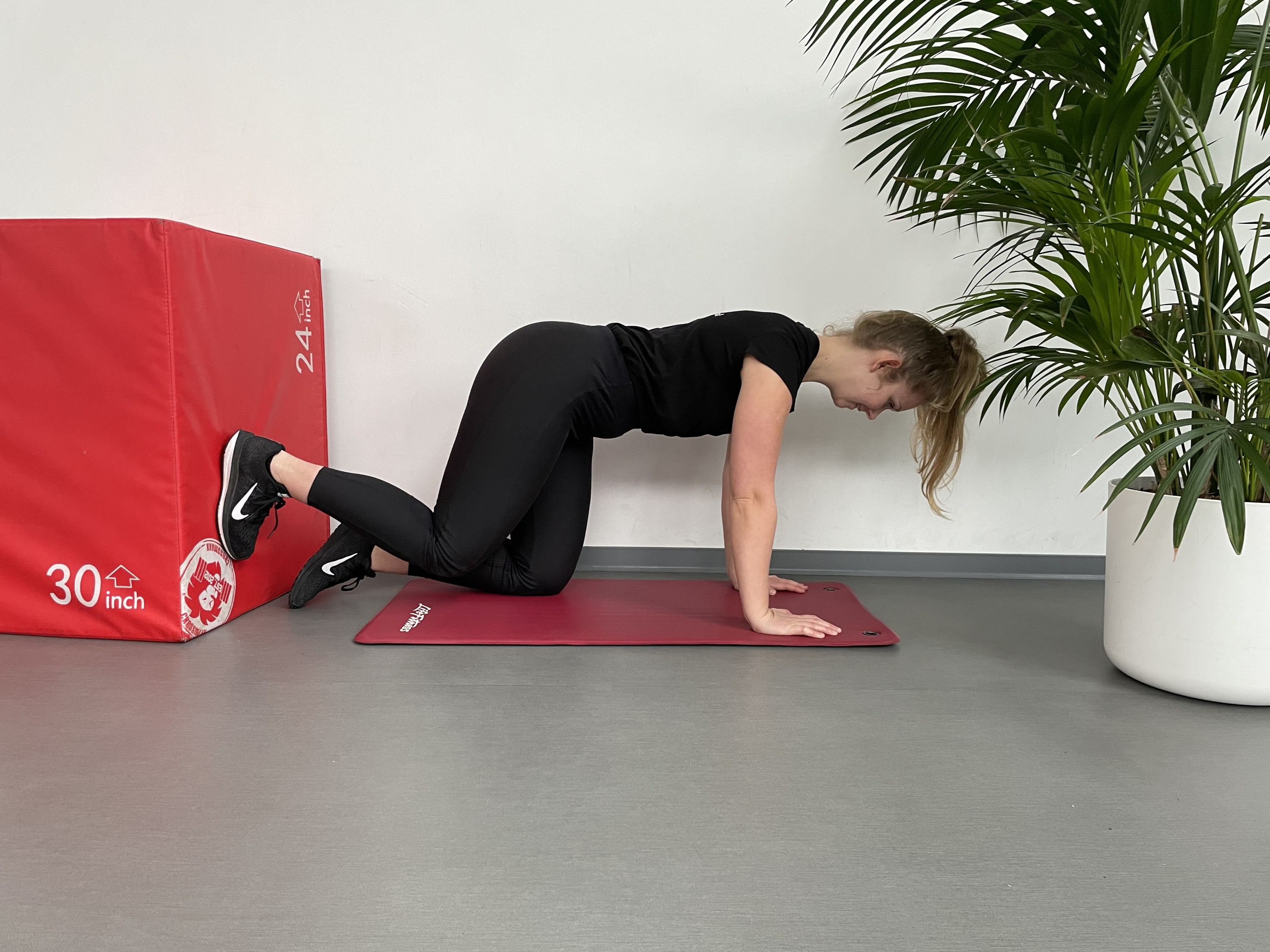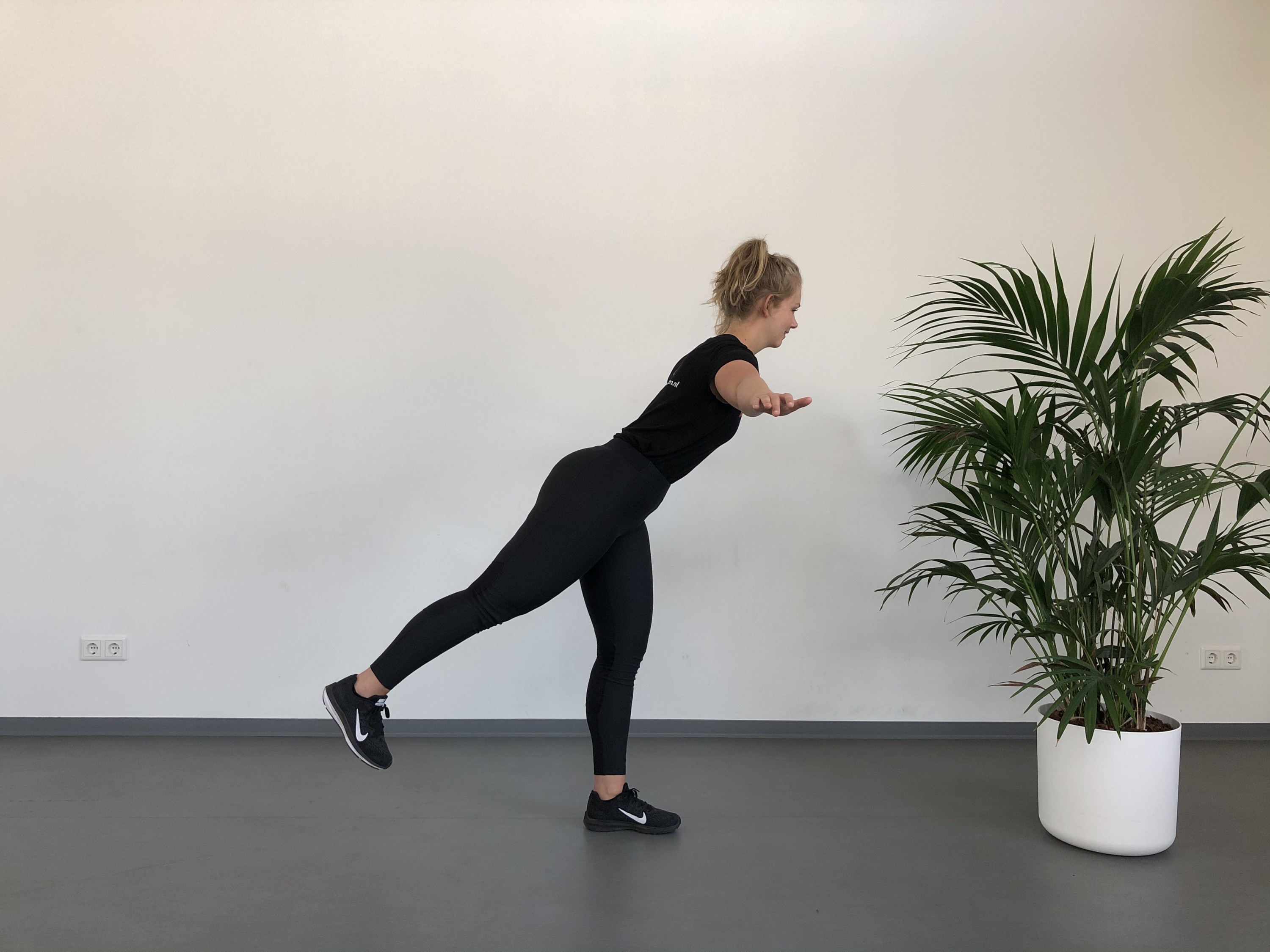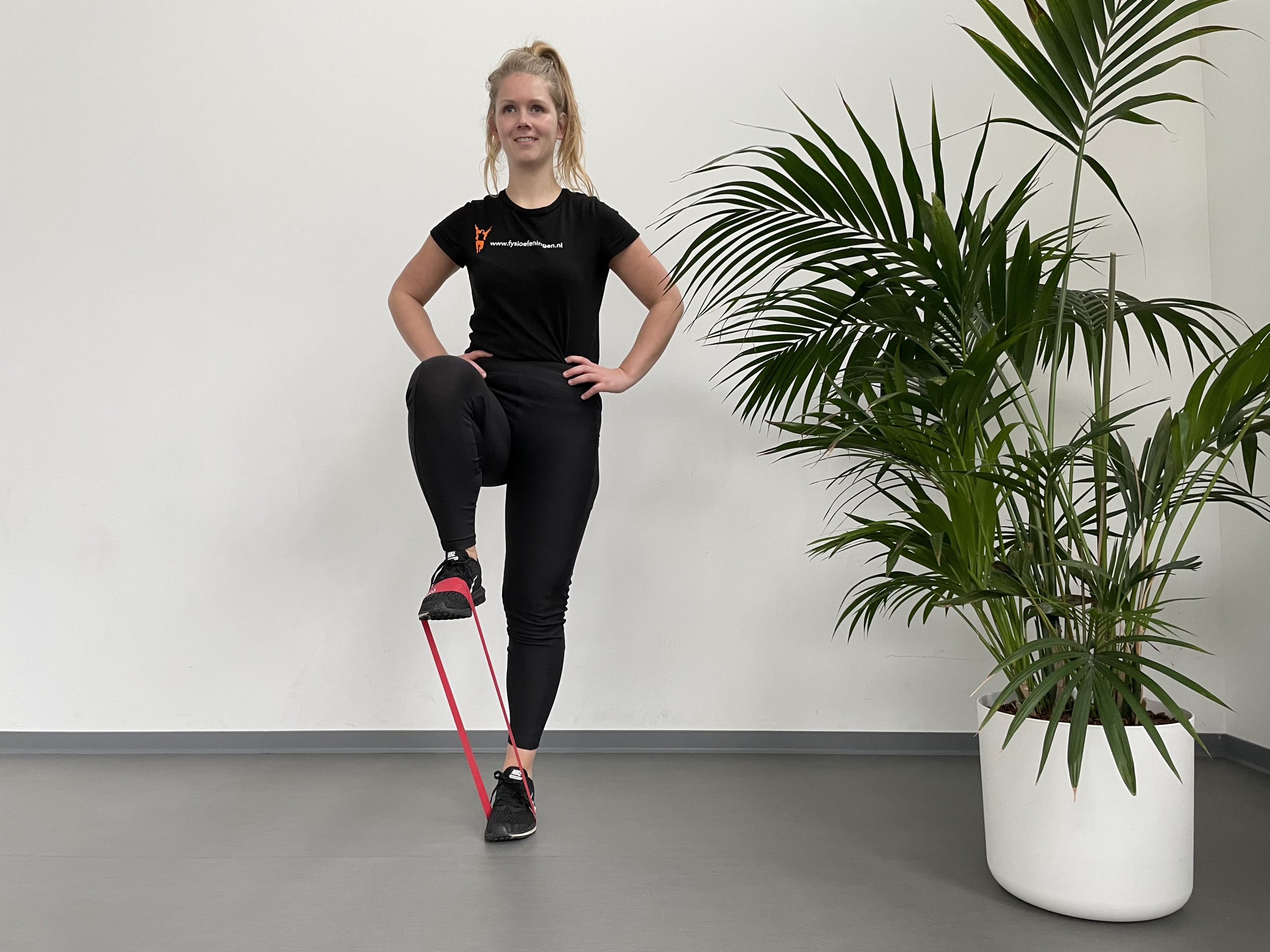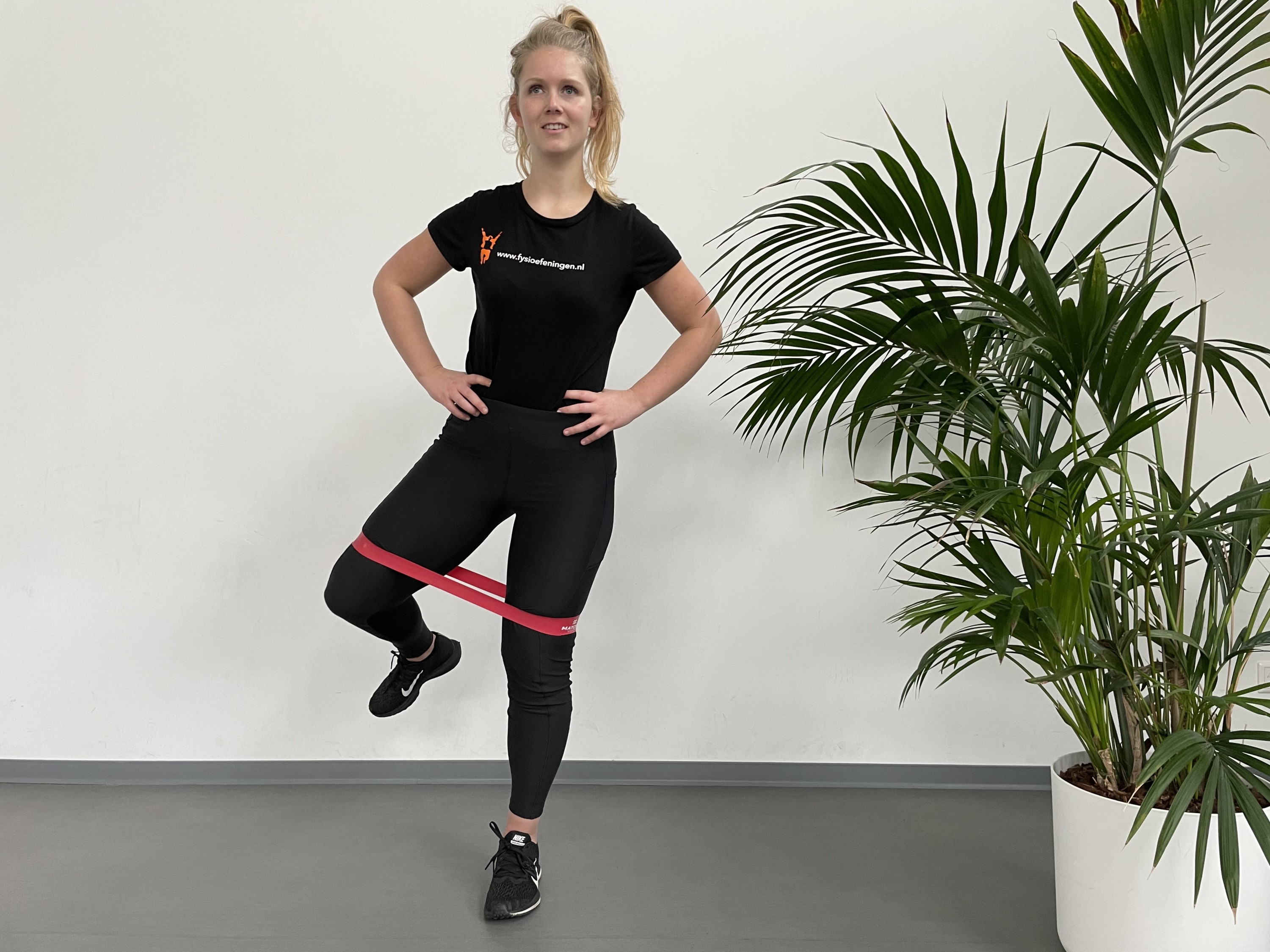
Hip injuries
The hip joint is made up of two bones, the thigh bone (femur) and the hip bone (os coxae). The two os coxae together with the sacrum make up the pelvis. The hip bones on both sides of the pelvis contain the hip socket called acetabulum. There is a lot of different hip injuries. Here you can find more information or exercises.
Fitness mat
Hard. Compact. Qualitatively.

Step
Hard. Compact. Qualitatively.

The hip
The hip joint is made up of two bones, the thigh bone (femur) and the hip bone (os coxae). The os coxae is formed by three different hip bones (pubic, ilium and ischium). The two os coxae together with the sacrum make up the pelvis. The hip bones on both sides of the pelvis contain the hip socket called acetabulum. The socket is larger than the ball (head of femur) and ensures the ball can not dislocate easily. There is a slight vacuum in the hip joint producing suction further helping the ball stay in the socket. There can be a lot of load over the hip joint and this suction helps to keep the ball stable in the socket.
There is a variety of hip injuries and they can be categorized in specific or non-specific injuries and in acute or chronic injuries. Besides injuries of the hip joint a number of other conditions can cause pain in the hip region. Examples are an inflamed bursa (trochanteric bursitis), referred pain, a broken hip or a torn hip flexor.
Acute hip injuries: the injury occured within the last 6 weeks. There was an acute moment; for instance a fall, overuse on a long walk or after an intense game.
Chronic injuries: these injuries persist for longer than 3 months and include: osteoarthritis of the hip, bursitis or hip dysplasia. Contrary to popular belief, chronic hip pain can often be treated. Physiotherapy can be very effective in reducing or resolving your chronic or acute hip pain.
In short: a number of hip injuries can occur. The quality of the cartilage can deteriorate (osteoarthritis) which is a normal aging process. Various factors can increase the risk of torn muscles, bruises, stiffness, movement restrictions and instability. It is important to find the cause of the injury so treatment and training can be targeted to your specific injury.







